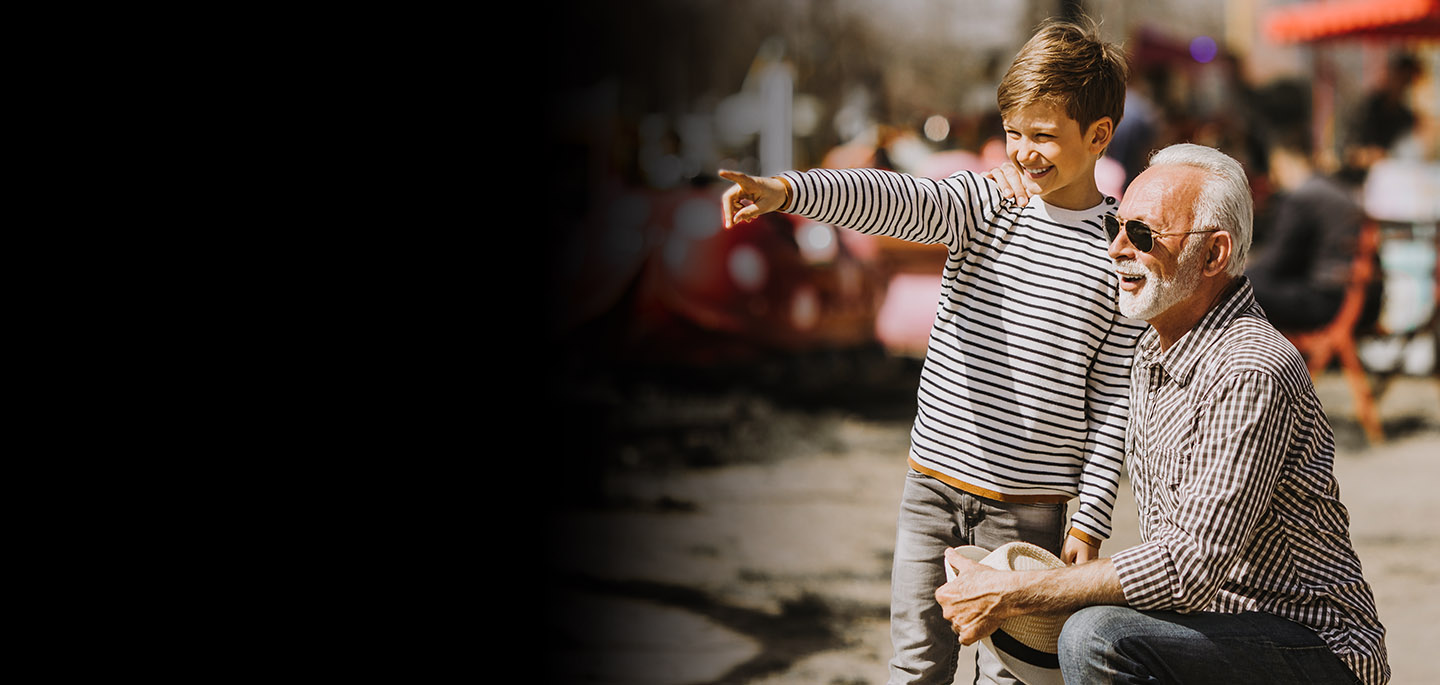
UPGRADE your hearing;
UPGRADE your life!
- Complimentary Hearing Evaluation
- Free in-home trial
- Get $500 Off Phonak Lumity Hearing Aids
Find a location nearest you!
At Tri-County Hearing, we make it easy to get expert care.
Visit our clinic locator to book a hearing test or hearing
consultation online.
- In Person
- Curbside
- Virtual

UPGRADE your hearing experience today!
For those that are considering hearing aids for the first time or thinking about an upgrade of existing devices, we take a personalized approach to ensure that you receive personalized attention and solutions that suit you. Take advantage of our latest discount – up to $500 off the latest in Phonak technology – and schedule your appointment today.
Expert care
starts here.
At Tri-County Hearing, we pride ourselves on hiring great hearing professionals who love helping patients improve how they hear the world. That's why we take a comprehensive approach to your care. We start with the latest diagnostic procedures to understand the precise sources and effects of your hearing loss. Only then do we recommend treatment with state-of-the-art solutions, custom prescribed and fitted for your lifestyle.
We treat common hearing loss & protection needs.
Each care plan is prescribed and fit for your life style.
-
Workplace
You use a hardhat to protect your head, work gloves to protect your hands, and safety glasses to protect your eyes. What are you using to protect your ears? Our Workplace Hearing Protection range offers compact and lightweight options, designed for comfortable everyday wear.
Learn more -
Social
The small pleasures of daily life – having a phone conversation, laughing at a joke during dinner, or listening to your grandchildren – can be within your reach again with our hearing solutions.
Learn more -
Music Lovers
Whether you’re a working musician trying to protect your ears or a music lover who wants to hear their favorite song again, we have hearing solutions for you. From prevention and protection to treatment and solutions, we’re ready to help.
Learn More
Enjoy a Life Worth Hearing.
Click below to take the next step in your hearing journey!